Brief About ESA’s ALTIUS Mission
The Earth’s ozone layer is crucial for sustaining human life on Earth; it acts like a natural sunscreen for our bodies. It protects us from toxic UV rays from the sun that cause severe damage to our bodies.
ESA’s upcoming project ALTIUS aims to monitor the distribution and evolution of stratospheric ozone & other atmospheric molecules important for climate research.
ALTIUS, this mission was proposed by a Belgian institute and is currently being developed by the ESA. It is expected to launch in 2026 with the Vega-C rocket and carry three imagers: ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), and near-infrared (NIR).

By using solar, stellar, and lunar occultation technology, ALTIUS will achieve every three-day coverage from sun-synchronous orbit at 668 km. This mission supports weather forecasting, validates int’nal agreement of the Montreal Protocol.
ALTIUS Mission Objective: Is to monitor the distribution & evolution of stratospheric ozone in the Earth’s atmosphere.
Technology Behind ALTIUS Mission: How it’s Tracking the Stratosphere From Space?
ESA’s ALTIUS Mission is built to monitor the distribution and evolution of the stratospheric ozone layer using advanced technology. Key technology using the ALTIUS mission….
- Advanced Spectral Filtering
- Acousto-optic tunable Filters(AOTFs): Used in the VIS and NIR channels, AOTFs allow rapid and precise selection of narrow spectral bands for imaging.
- Fabry-Perot Interferometers(FPIs): Used in the UV channel, FPIs provide high spectral resolution filtering and enable the detection of subtle features in atmospheric spectra.
- Multiple Observation Modes
- Bright Limb: Observes the sunlit atmospheric limb.
- Solar Occultation: Measures sunlight passing through the atmosphere during sunrise or sunset from the satellite’s perspective.
- Stellar Occultation: Observes starlight passing through the atmosphere, useful during the night side of the orbit.
- High-Resolution 2D Imaging
- ALTIUS carries a high-resolution 2D imager that observes the Earth’s atmosphere from the side, specifically targeting the limb(the atmosphere boundary seen from space).
- Hyperspectral Imaging Spectrometer
- A hyperspectral imaging spectrometer is an advanced detection device that combines imaging and spectroscopy to collect detailed spectral information for every pixel in an image.
- A hyperspectral imaging spectrometer is an advanced detection device that combines imaging and spectroscopy to collect detailed spectral information for every pixel in an image.
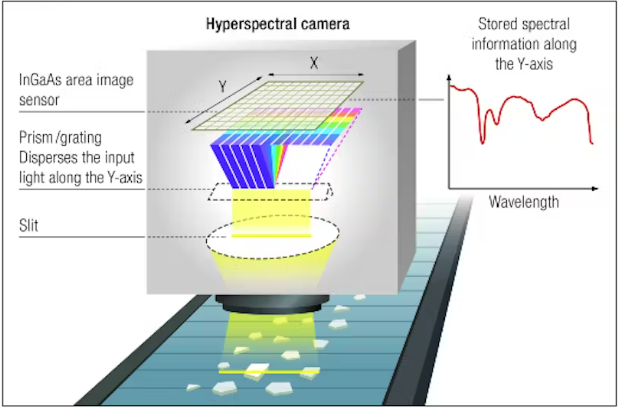
- Limb Sounding Technology
- Limb sounding is a remote sensing technique used by satellites to observe the Earth’s atmosphere by looking at the “limb,” or edge, of the planet.
The Role of the ALTIUS Mission in Fighting Climate Change And Ozone Depletion
ALTIUS is a European Space Agency (ESA) satellite mission designed to address two critical environmental challenges: climate change and the depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer.
- Ozone Depletion: The ALTIUS Mission will provide continuous, high-resolution data on the distribution of ozone in the stratosphere. The ALTIUS mission provides critical data that ensures the scientific community can track ozone layer recovery and variability.
- Climate Change: ALTIUS will monitor greenhouse gases and aerosols in the stratosphere, and ozone itself plays a dual role in climate. While ozone depletion leads to surface cooling, tropospheric ozone contributes to warming as a short-lived climate pollutant. The mission’s data helps refine atmospheric models, improve weather forecasting, and enhance our understanding of ozone recovery.
Highlight Tracking Ozone & Greenhouse Gas Helps Enforce International Norms.
Monitoring ozone and greenhouse gases is essential for international agreements like the Montreal Protocol and its amendments, along with climate-focused agreements like the Paris Agreement.
- Accountability: Regular tracking lets us see if countries are living up to their promises to cut down on harmful gases. If the numbers don’t add up, it’s a clear sign that something needs to change.
- Early Warning: By monitoring the atmosphere, scientists can quickly spot any unusual spikes in pollution. This helps catch illegal or accidental emissions before they become bigger problems.
- Building Confidence: When everyone has access to the same data, it creates a sense of fairness. Countries are more likely to cooperate and stick to the rules when they know they’re all being watched equally.
- Guiding Action: Reliable information helps leaders make smart choices about environmental policies and improvements. It’s the foundation for stronger laws and better protection for our planet.
In a nutshell, tracking ozone and greenhouse gases is like having a global watchdog. It keeps everyone honest, helps solve problems fast, and supports a healthier Earth for everyone.
Thank you so much for reading! Glad you like it and found it helpful. Your support means a lot to me. Please share your thoughts in the comments below. Don’t forget to share this post with others who might enjoy it too!
